Do you ever feel like your advertising budget is not being used effectively? You set up your campaigns, target an audience, and hope for the best. But what if there is a way to maximize your return on every single impression? In today’s fast-moving digital advertising world, staying competitive requires embracing new technologies and efficiency.
Just imagine being able to reach your ideal audience with great precision and at the best possible time. This is not just a dream; it’s made possible by ad server and real-time bidding (RTB).
It’s hard to believe how ads were managed by advertisers and publishers three decades ago when we see how advanced and efficient today’s ad technologies are. Here is how it works today: When someone visits a website, there is a quick auction where advertisers bid to show their ad. This split-second auction ensures that your ad is seen by the right people, making your ad efforts more effective and profitable.
Ad servers manage and deliver these ads smoothly, while real-time bidding (RTB) decides the best placement for them. Together, they transform the way digital advertising is executed, making every effort valuable. Want to learn more about Ad servers and RTB? Check out this blog to get a deeper understanding of how they revolutionize digital ad effectiveness.
Ad Server: The Backbone of Digital Advertising
Before the internet, advertising involved a lot of paperwork and was quite complicated. When online advertising started over 30 years ago, it promised to make things easier by moving operations online. However, the digital advertising landscape grew rapidly, making things even more complicated.
With more publishers, advertisers, and consumers involved, traditional advertising struggled to keep up. To address this, forward-thinking professionals started building the foundation for what would become the backbone of digital advertising: ad server. Now, they are crucial for managing most online ad placements.
Here is the Real Meaning
An advertising server is an advanced tech platform that handles online ads for websites, apps, and digital platforms. It’s like a control center where advertisers, publishers, and ad agencies organize campaigns. Its main job is to show online ads to the right people, using info like location and interests. It also monitors the performance of ads, tracking views, clicks, and sales, which helps everyone determine whether their ads are effective or need adjustments.
For Advertisers
Ad servers assist advertisers by efficiently managing and distributing their online ads across various digital platforms. They create their ad campaigns and target specific audiences, and then the ad server acts like a smart matchmaker, finding the right ad for the right viewer on a publisher’s site. This laser focus helps them reach the most likely customers, track results, and fine-tune their campaigns for maximum impact.
For Publishers
Ad servers are essential for publishers to manage their ad inventory effectively. They sell ad space, choose the best ad for each user, and maximize revenue. This targeted approach not only boosts user experience but also attracts high-paying advertisers.
The Birth of the Ad Server: How Online Advertising Took Off
Ad servers were first introduced around 1995, in the early days of online advertising. Their main function was to help publishers manage and control the delivery of online ads. Initially, ad targeting was limited, relying on basic header information collected from users’ browsers, such as:
- Language settings
- Page URLs
- Browser type and version
- Operating system
Now, the question arises of who founded the ad servers. FocaLink Media Services, established by Dave Zinman, Andrew Conru, and Jason Strober, pioneered this field by setting up what could be considered the first ad server in 1995.
Evolution Of Ad Server
Ad servers have come a long way since they appeared. They have changed a lot to keep up with what advertisers and publishers need for a successful ad campaign. As we already learned, advertisers and publishers can now do things like target specific audiences, manage budgets, and control how often ads are shown.
These capabilities have also been integrated into newer platforms like Demand-Side Platforms (DSPs) and Supply-Side Platforms (SSPs), demonstrating the continuous improvement and integration of ad technology over time.
Advertising Servers Categories: First-Party and Third-Party Ad Servers
First-party and Third-Party ad servers are the two primary categories of advertising servers used in online advertising. Each serves distinct purposes and roles, which are given below:
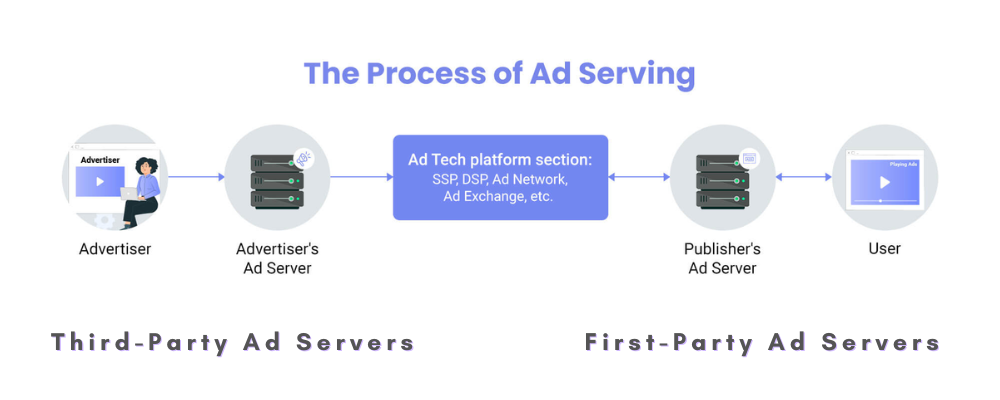
First-Party Ad Server
A first-party advertising server, also known as a publisher-side advertising server (ad server for publisher), is a tool used by website and app owners (publishers) to manage their ad inventory and display targeted ads to their users. It acts as a command center for the ads on a site.
Here’s how it works
The advertising software runs on a physical server, either owned by the publisher or provided by an ad tech company. When a user accesses the publisher’s website or app, the advertising server receives a request to fill the ad space.
The server then considers various factors, such as the user’s browsing history or the content of the page, and selects the most relevant ad from the publisher’s inventory. This inventory can include ads sold directly to advertisers or those obtained through programmatic buying (automated auctions).
There are numerous types of first-party advertising servers designed to meet specific needs:
- Open-source- Free to use but require technical expertise for setup and maintenance.
- Display- Manage standard banner ad text ads.
- Video- Handle various ad formats, including pre-roll, mid-roll, and post-roll ads.
- Mobile- Optimized for displaying ads on smartphones and tablets.
- Native- Deliver ads that seamlessly blend with the surrounding content.
- Rich media- Support interactive ad formats.
By utilizing a first-party advertising server, publishers obtain more control over their ad space, enabling them to:
- Increase revenue
- Enhance user experience
- Acquire valuable data
- Third-Party Ad Server
Third-Party Ad Server
A third-party advertising server functions as a manager for advertisers, taking care of the technical aspects of their online ad campaigns. Advertisers or media agencies use this server to upload their ad creatives, manage their campaigns, and track the outcomes.
Here’s how it operates
When advertisers want to run ads on various websites, instead of directly uploading their ads to each site, they use third-party advertising servers. This server stores the advertiser’s creatives and works with other ad platforms (used by website owners) to deliver the ads to the appropriate places.
It serves as a central hub for the advertiser’s ad campaign, allowing them to control everything from one location and efficiently manage multiple campaigns across different ad serving platforms. These servers are typically equipped with features to aid with ad targeting, performance reporting, and testing of different ad variations.
The “third party” in the name indicates that the server is a separate entity from both the advertiser and the website owner. It sits in the middle, assisting the advertiser in effectively reaching their target audience.
Ad Servers vs. Real-time Bidding: What’s the Link?
If we talk about the advertising servers and real-time bidding, they both work differently, but there is a solid connection between them. They both have a close relationship in the context of online advertising. Both are vital components of the digital advertising ecosystem and collaborate to optimize the delivery and performance of online ads. Here’s the role that they perform in an ad ecosystem:
Advertising Servers
They are tech platforms that manage the delivery of advertisements to websites, mobile apps, or other digital platforms. They perform several key functions:
- Storing Ad Creatives- Advertising servers store the content of ads, such as images, videos, and text.
- Ad Delivery- They display ads to users based on specific criteria like targeting options, how often the ads appear, and the schedule for showing them.
- Tracking and Reporting- Advertising servers keep track of how many times ads are seen, clicked on, and interacted with. They also give detailed reports on how well the ads are doing.
Real-Time Bidding
Real-time bidding is a process in which digital ad impressions are bought and sold through automated auctions in real-time. We can say that it is a fully automated system in which advertisers compete in auctions for individual ad impressions just before they appear on a website or app.
This system enables highly targeted advertising based on various factors. It is a matter of a few seconds where advertisers have to decide whether they want to display their ad and how much they are willing to pay for that impression. The winning bidder’s ad is then displayed. This process involves multiple components:
- Supply-Side Platforms- Supply-side platforms (SSPs) assist publishers in selling their ad inventory by connecting them to multiple ad exchanges.
- Demand-Side Platforms- Demand-side platforms (DSPs) allow advertisers to purchase ad space from numerous publishers through a single interface.
- Ad Exchanges- Ad exchanges help with the auction process, where bids from advertisers (DSPs) are paired with available ad spaces from publishers (SSPs).
Relationship Between Ad Servers and Real-Time Bidding
As we understand their different purposes in an ad ecosystem. Now it is time to look at how they linked with each other:
Inventory Availability
Advertising servers provide information about available ad inventory to SSPs, which then relay this information to ad exchanges. This is the starting point for the real-time bidding process, where impressions are made available for bidding.
Ad Selection and Delivery
When an ad impression becomes available, an ad request is sent to the ad exchange. Demand-side platforms (DSPs) bid on this impression based on targeting criteria and budget constraints. The top bid wins, and the winning ad is delivered to the user via the ad server.
Observation and Analysis
Once the ad is delivered, the advertising server keeps track of the ad’s performance, such as impressions, clicks, and conversions. This data is important for advertisers to evaluate the success of their campaigns and for publishers to manage the value of their ad inventory.
Optimization
The data collected by advertising servers from delivered ads are utilized to optimize future bidding strategies. Advertisers can adjust their bids and targeting criteria based on the performance data provided by servers.
Importance of Real-Time Bidding in Digital Advertising
Here are some key points on the importance of Real-Time Bidding (RTB) in digital advertising for publishers and advertisers. Please take a moment to explore these points:
The Significance of RTB for Publishers
- Increased Revenue and Fill Rates- RTB (Real-Time Bidding) opens up your ad inventory to a large pool of advertisers who compete in real-time auctions. This competition helps increase the prices for your ad space, which may lead to higher CPMs (cost per mille) and overall revenue. Additionally, RTB helps fill unsold ad inventory by attracting more buyers, thus reducing empty spaces on your website and app.
- Real-Time Campaign Optimization- By using RTB, you can gain valuable insights into real-time ad performance. This helps publishers to see which ad types, placements, and audiences generate the most revenue. It enables constant optimization of your ad strategy to maximize your income and attract the most valuable advertisers.
- Greater Control and Transparency- Although real-time bidding (RTB) involves automation, this does not imply losing control. You can establish minimum bid prices (also known as floors) to guarantee that your ad space sells for an acceptable price. Besides, RTB platforms offer thorough reporting on the purchasers of ad space on your site, enabling you to make well-informed decisions about potential partnerships.
The Significance of RTB for Advertisers
- Cost-Effective Bidding- RTB allows advertisers to bid only on individual ad impressions that match their criteria. This prevents them from wasting money on ad placements that aren’t relevant. Additionally, the RTB process ensures that advertisers pay the lowest price possible for each impression, helping them maximize their return on ad spend (ROAS).
- Real-Time Data- RTB provides advertisers with real-time data on ad performance. They can see which demographics, devices, and placements generate the best results. With this information, they can adjust their bids and targeting strategies accordingly. This continuous optimization ensures that their ad campaigns constantly improve and deliver the best possible results.
- Increased inventory Access- In traditional ad buying, advertisers negotiate directly with publishers for specific ad placements. On the other hand, RTB offers a wide range of ad inventory on numerous websites and apps. This allows advertisers to reach highly relevant audiences that they may not have reached otherwise, thereby maximizing their potential customer base.
Conclusion
Ad servers and real-time bidding (RTB) have revolutionized digital advertising. Advertising servers manage ad delivery and track performance, while RTB uses auctions to ensure ads reach the right audience at the right price. Together, they benefit both publishers and advertisers.
Publishers can maximize revenue and fill ad space, while advertisers can effectively target their audience and optimize ad campaigns for better returns. By employing these technologies, advertisers and publishers can streamline ad delivery, optimize targeting, and maximize ROI.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an ad server?
An advertising server is an ad tech platform that functions as a central control system for online advertising. It oversees the placement of ads on websites and apps, selecting the appropriate ad to display to a specific user at the right time.
What is real-time bidding (RTB)?
Ans. RTB is a process in which advertisers bid on individual ad impressions in real-time, just before they appear on a website or app. It’s like an automated auction for ad space.
How do ad servers and real-time bidding work together?
Ans. Advertising servers manage the delivery of ads and track their performance, while RTB uses real-time auctions to bid for ad space. They work together to maximize advertising efficiency.
What are the two primary categories of advertising servers?
Ans. The two main types of ad servers are first-party advertising servers (used by publishers) and third-party advertising servers (used by advertisers).
What are Demand-Side Platforms (DSPs) and Supply-Side Platforms (SSPs)?
Ans. DSPs allow advertisers to buy ad space from multiple publishers through a single interface, while SSPs help publishers sell their ad inventory by connecting them to multiple ad exchanges.